15 change management models to know about in 2025
Facing friction in IT transformation? Explore Freshservice's change management capabilities to see if it's the right fit for your goals.
Jun 10, 20259 MIN READ
Transformation journeys do not simply stumble. They often face complete derailment. 96% of them encounter challenges so big that they threaten to throw everything off course1. In 2025, navigating such a journey demands precision and foresight.
Let’s explore 15 change management models built for volatility, each designed to help organizations navigate uncertainty, drive transformation, and build resilience in ever-changing environments.
What are change management models?
Change management models are structured frameworks that guide your business through periods of transition. This transition could be structural, technological, cultural, or strategic. Change management models are primarily designed to align people, processes, and strategies for effective transformation.
Change management, while inevitable, is rarely easy. Change management models, with clearly defined stages, stakeholder strategies, and feedback loops, help minimize resistance and facilitate smoother adoption of desired changes.
Over time, change management models have evolved from rigid step-by-step plans to more fluid, adaptive systems. Today, these models reflect the realities of hybrid work and digital transformation, balancing it all with human complexity.
Why use change management models?
Without a proven framework, change can seem chaotic and unpredictable, creating uncertainty and resistance throughout the organization. But a structured and proven model helps:
Build stakeholder trust
Accelerate buy-in
Minimize risks such as misalignment and communication breakdowns
Consider Nokia’s decline. Rapid market shifts met with internal inertia. In contrast, “Satya Nadella's leadership in Microsoft is a model of transformational leadership, which has been known to be the most crucial when there are rapid changes in technology and market requirements.” 2
The difference? A clear roadmap versus guesswork. Proven models don’t guarantee success, but they significantly increase the chances of achieving it.
Sign up for Freshservice today
Get a hold of the intuitive, flexible, and easy-to-use Change Management Software.
Overview of popular change management models
Popular change management models offer systematic approaches that assist organizations in managing transitions, reducing resistance, and enhancing the likelihood of successful change adoption. The models explained below have become trusted tools for guiding transformation with clarity and intent.
S. no. | Model | Best for | Key strength | Focus area | How to implement |
1. | Lewin’s Model | Process-driven environments | Simplicity and structure | Organizational change | Communicate urgency, break old norms, stabilize |
2. | Kotter’s 8-Step | Enterprise-wide transformation | Momentum building | Leadership and culture | Follow each step with visible leadership support |
3. | ADKAR | Individual adoption | Personal change diagnostics | People | Assess individuals, address gaps at each stage |
4. | McKinsey 7-S | Org redesign, M&A | Holistic alignment | Systems and culture | Audit all 7 elements, align for strategic fit |
5. | Bridges’ Model | HR and leadership shifts | Emotional support | Transition psychology | Provide emotional guidance across each phase |
6. | Nudge Theory | Decentralized teams | Subtle behavioral influence | Behavior | Redesign environments to guide decisions |
7. | Kübler-Ross Curve | Emotional transitions | Empathy and emotional pacing | Psychology | Map reactions, offer phased emotional support |
8. | Satir Change Model | Team coaching, agile shifts | Performance-emotion dynamic | Team dynamics | Normalize chaos, support through integration |
9. | Resistance to Change | Change diagnostics | Targeted resistance management | Risk mitigation | Identify resistance type, tailor interventions |
10. | PDCA Cycle | Operational or iterative change | Continuous improvement loop | Process | Iterate through small, data-led experiments |
11. | Stephen Covey Model | Leadership and values alignment | Vision and trust | Personal leadership | Align changes with core values and habits |
12. | Kaizen Model | Lean, cultural shifts | Grassroots engagement | Continuous improvement | Empower staff to make small daily improvements |
13. | LaMarsh Model | Regulated, high-risk industries | Stakeholder impact clarity | Risk & structure | Define agent roles, assess risk, track impact |
14. | John Fisher Model | Coaching and L&D | Personalized emotional tracking | Emotions in change | Use curve to guide support and coaching plans |
15. | Maurer’s Resistance Model | High-resistance environments | Root-cause resistance resolution | Relationship dynamics | Diagnose resistance level, engage accordingly |
1. Lewin’s Change Management Model
One of the earliest frameworks, Lewin’s model breaks change into three stages:
Stage 1: Unfreeze
Loosen old behaviors.
Stage 2: Change
Move to new, desirable ones.
Stage 3: Refreeze
Solidify them.
The model focuses on preparation before action and consolidation afterward. It is especially effective in traditional, process-driven environments that benefit from clear staging.
2. Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
This model thrives in environments where structure and leadership sponsorship drive change. Each of the following steps builds momentum, and emphasizes communication, empowerment, and short-term wins.
Highlight the need for change through data or risks to spark motivation.
Form a strong, influential team to lead and support the change.
Develop a clear vision and actionable steps to guide the change.
Gain broad-based support by engaging people emotionally and rationally.
Eliminate obstacles and empower people to act.
Deliver visible, quick successes to build momentum.
Use early wins to push further change, adjusting systems and structures as needed.
Embed new behaviors into culture through reinforcement and leadership continuity.
3. ADKAR Model
ADKAR stands for Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement. First, people must understand the need for change (awareness) and be motivated to support it (desire). Then, they need the know-how (knowledge), the skills to act (ability), and consistent encouragement to sustain it (reinforcement).
ADKAR works by identifying gaps in these areas and targeting interventions to help individuals adopt and maintain the change effectively.
4. McKinsey 7-S Framework
This change management framework examines structure, strategy, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff.
Here’s what it means:
The model answers questions like: How is the company organized? Who reports to whom? What is the formal framework?
It evaluates decisions about markets, products, growth, and how to respond to changing environments.
Systems support the structure and strategy in practice. The model also examines the daily processes and procedures that employees use to get work done, including IT systems, communication channels, and operational workflows.
Shared values sit at the center of the model and influence all other elements. They are the core beliefs, norms, and culture that guide employee behavior and organizational priorities.
The model helps you understand: What skills do the people have? What are the organization’s distinctive capabilities or core strengths?
It reflects how leaders behave and interact with staff and how that shapes the work environment.
Finally, the model focuses on the people within the organization, their demographics, recruitment, development, and motivation. It considers whether the organization has the right people in the right roles.
5. Bridges’ Transition Model
This model distinguishes between change (external events) and transition (internal psychological process), moving through endings, the neutral zone, and new beginnings.
Stage | What it is | What it means |
Endings | Letting go of the old ways, roles, or identities | Involves loss and resistance; emotions like fear, denial, anger, or sadness may surface |
Neutral zone | The in-between phase where the old is gone but the new isn’t fully formed | A time of uncertainty and low clarity, but also creativity and opportunity for innovation |
New beginnings | Embracing the new direction, roles, or mindset | New energy, purpose, and commitment emerge; people begin to perform well and feel confident again |
6. Nudge Theory
Derived from behavioral economics, Nudge Theory is about influencing behavior subtly rather than mandating it. It relies on designing choices that encourage better decisions without coercion. In organizational change management, nudges can guide adoption through cues, defaults, and social proof.
7. Kübler-Ross Change Curve
Originally a model of grief, the change curve illustrates the emotional journey individuals undergo: shock, denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance, and integration.
It’s valuable for anticipating emotional responses and planning support. Often used in layoffs, restructuring, or emotionally charged changes, this model brings empathy into planning.
8. The Satir Change Model
Satir’s model is useful for coaching teams through volatile phases of transformation. It captures how performance dips before it improves during change:
Old status quo: A stable, familiar phase where existing patterns dominate. People are comfortable but may be stagnant.
Resistance: A change is introduced, triggering fear, denial, or pushback as people resist leaving their comfort zone.
Chaos: Old ways no longer work, but new ones aren’t yet in place. Performance dips, emotions run high, and uncertainty prevails.
Integration: People begin experimenting with and adopting new behaviors. Confidence and competence slowly return.
New status quo: Stability is restored at a higher level of functioning, with new norms and improved performance.
Resistance to Change Model
This framework categorizes resistance into logical (data-based), psychological (emotional), and sociological (cultural) barriers. It helps diagnose resistance drivers and plan targeted interventions. The framework is most effective when layered into broader models like ADKAR or Kotter to address barriers proactively and personally.
10. The PDCA Cycle
Plan-Do-Check-Act is a continuous improvement loop that supports incremental change. It’s pragmatic, data-driven, and rooted in quality management. Especially effective in operations, manufacturing, or process improvements, PDCA supports an experimental mindset where learning informs change.
11. Stephen Covey Model
Inspired by Stephen Covey’s book The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People, this model centers on personal leadership and proactive behavior. It emphasizes aligning change with values, vision, and trust. Often used in leadership development or team transformation, it connects self-awareness with organizational impact.
12. Kaizen Model
Kaizen, or "continuous improvement," focuses on small, consistent, incremental changes involving everyone in the organization. It thrives in lean environments and empowers employees to take charge of improvements.
13. LaMarsh Model
This is one of the best change management models for adding discipline and foresight to complex change programs. Rooted in the LaMarsh Managed Change methodology, this model:
Emphasizes proactive planning, stakeholder impact analysis, and risk mitigation.
Drives accountability and measurability (with clearly defined change agent roles) to help embed lasting change with clarity and control
14. John Fisher Model
Fisher’s Personal Transition Curve maps emotional reactions from anxiety to threat, guilt, acceptance, and growth. It highlights how individuals process change at different speeds. It’s often used alongside coaching and training to personalize support and foster resilience.
15. Maurer’s 3 Levels of Resistance and Change Model
Change advisor, speaker, and author Rick Maurer categorizes change resistance into three levels:
I don’t get it (information gap)
I don’t like it (emotional resistance)
I don’t like you (relationship resistance)
This model is among highly effective change management methodologies as it helps you identify the root cause of resistance rather than just the surface reaction.
Once you understand the cause and source of resistance:
You can tailor your communication and strategies accordingly.
Increase the chances of successful change adoption and reduce conflict.
Looking to start ITCM in your organization?
How to choose the right change management model
Choosing the right change management model involves assessing the organization's specific needs, culture, and the scale of change to ensure alignment with the desired outcomes.
Selecting the right model depends upon several factors:
Your organizational culture
The scale of your change initiative
The desired speed of transformation
Your organizational readiness (how prepared your people, systems, and leadership are for change)
Stakeholder alignment
Your model should offer enough flexibility to adapt to the unique dynamics of your team structure and strategic goals.
Implementing a change management model successfully
Successfully implementing a change management model requires clear communication, strong leadership, and ongoing support to guide employees through each stage of the transition. Here are some change management best practices illustrating how you can roll out your change management models effectively:
Step 1: Map the change journey
Align the model’s stages with your organizational goals, processes, and culture. Customize timelines and milestones to reflect the scale and complexity of the transformation. Clarity in this phase sets the foundation for all that follows.
Step 2: Engage leadership early
Leaders must do more than sponsor the change. They need to model it. Active involvement builds credibility and encourages buy-in from the top down.
Step 3: Communicate with purpose
Transparent, two-way communication reduces uncertainty and builds trust. Frame messages around the “why,” and tailor delivery for different audiences to ensure clarity and relevance.
Step 4: Deliver targeted training
Equip employees with skills, change management tools, and context needed to thrive post-change. Effective training addresses both the technical and emotional aspects of the shift.
Pro tip: Go beyond technical instructions in your training methods.
Contextualize the change, answer the “what’s in it for me,” and reinforce desired behaviors.
Use a mix of formats: live sessions, microlearning, job aids, peer mentoring, etc.
Pair this with a support system that includes accessible help channels, change champions, and ongoing coaching.
Step 5: Provide ongoing support
Reinforce progress with coaching, peer support, and open feedback loops. This continuous engagement sustains momentum and surfaces issues before they escalate.
Step 6: Measure, learn, refine
Track adoption metrics, gather qualitative insights, and assess business impact. Use what you learn to iterate and strengthen future change initiatives.
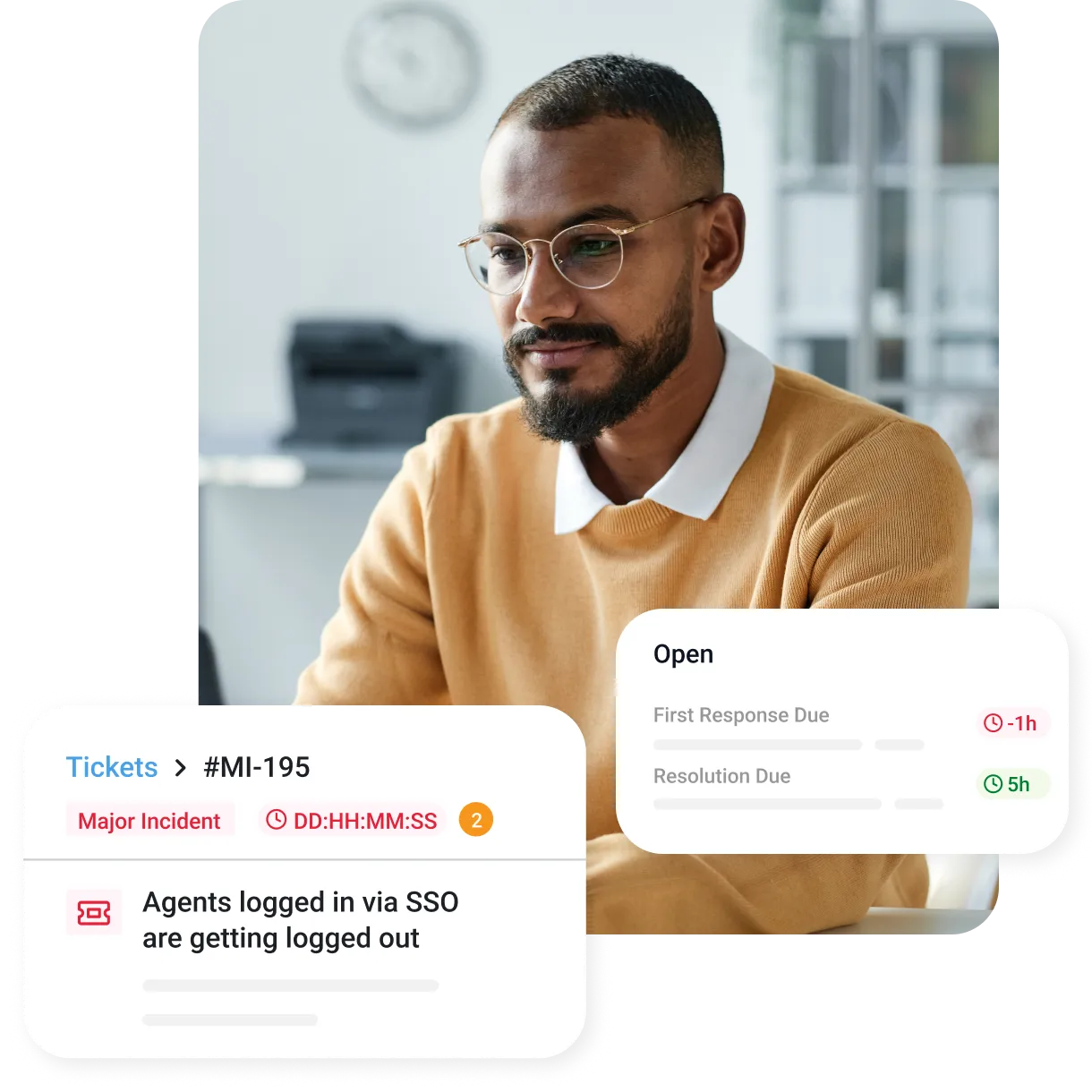
Transform your change management approach with Freshservice
Change management theories outline the strategies and processes used to guide an organization through periods of transformation. A seamless change management approach involves identifying key stakeholders, addressing resistance, and providing necessary training and resources to support the change.
By taking a structured approach, organizations can ensure smoother transitions and higher rates of successful adoption. Freshservice, with its intuitive change management features, can streamline this process by automating workflows, tracking progress, and ensuring better collaboration across teams.
Freshservice’s unified IT management platform includes dedicated capabilities to rollout and improve your change management end to end:
Freshservice equips you with intelligent workflows, automated approvals, built-in impact assessments, and real-time visibility.
It empowers you with built-in analytics to implement change initiatives efficiently while minimizing operational risks.
With seamless integrations and a structured framework, Freshservice provides better visibility and improved communication across teams. This empowers your organization to drive change confidently and with control.
Aiming to accelerate your organization’s change management strategy? Explore Freshservice’s capabilities and see if it’s the right fit for your team’s goals. Request a demo today.
Get a hold of the intuitive, flexible, and easy-to-use ITSM Software.
Related resources
No-nonsense guide to ITSM
Complete guide to ITOM
Level up the workplace with automation and AI
FAQs related to change management models
What are the three phases of change in change management models?
Most change management methodologies outline three core phases: preparing for change, implementing the change, and sustaining it. These stages help you manage transitions effectively and ensure long-term adoption.
Which change management model is best for large organizations?
Kotter’s 8-Step Model is ideal for large organizations due to its structured, leadership-driven approach that builds momentum and embeds change into organizational culture.
Can I combine different change management models?
Yes, combining models is common. Many organizations blend frameworks e.g. using ADKAR for individual adoption and Kotter for organizational alignment, to address both people and process dimensions of change.
What are the key factors for successful change implementation?
Successful change implementation depends on leadership commitment, clear communication, stakeholder engagement, adequate training, and ongoing support. Cultural alignment and readiness also significantly influence how well change is received and sustained.
How do change management models apply to digital transformation?
Change management models offer structure during digital transformation by guiding communication, strategy, adoption, and eventual integration. They help manage resistance and create a roadmap for sustainable technological change.
How long does it take to implement a change management model?
Implementation timelines vary based on scale and complexity. Small initiatives may take weeks, while enterprise-wide changes can span months.