Enterprise-grade ITSM, for every business
Give your IT, operations, and business teams the ability to deliver exceptional services—without the complexity. Maximize operational efficiency with refreshingly simple, AI-powered Freshservice.
Digital transformation—for every business
Transform IT from cost center to value creator with a powerful unified platform, time-saving automation, and fluid collaboration—enhanced with AI.
Unify IT, power business performance
IT now fuels business as well as support, so automating operations improves not only employee and agent efficiency, but also business continuity. By uniting teams and tools, you can reduce spending and complexity, and increase satisfaction from service desk to C-suite.
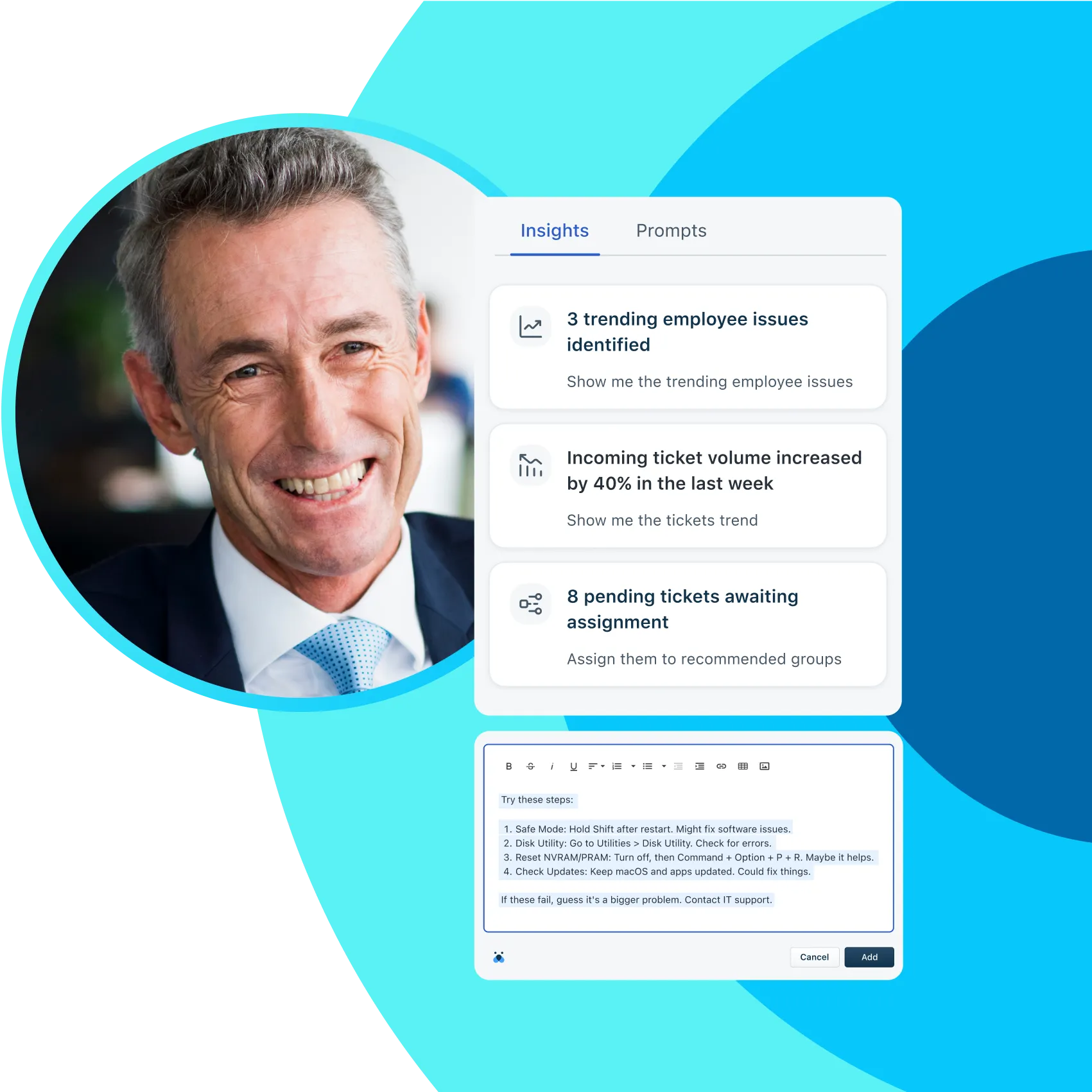
Built-in AI = Boosted efficiency, better experience
Make your staff, systems, and processes more efficient with built-in AI. Save time by automating routine queries and enabling self-service. Get performance insights and raise productivity with conversational prompts.
The power to be more productive
Freshservice enables you to save time with codeless drag-and-drop automations. Key workflows and integrations are also built in to offload low-value tasks, problem-solve, collaborate, and communicate better—and gain even more efficiencies in the future.
Freshservice capabilities
Automate, streamline, organize, and get more done—faster and easier than ever before.
See what’s newFreddy AI
Deliver self-service for customers, quicker resolutions for agents, and better insights for managers.
Omnichannel
Email to Slack, major incidents to password resets, see everything in one elegant, unified view.
IT service management
Seamless service management, efficiency with AI and automation, and insights for managers.
IT operations management
Consolidate, collaborate, and resolve fast with a unified solution, with AI to give you a boost.
ITAM
See it all in real time: hardware, software, and SaaS in an auto-updating CMDB
IT modernization
Automate and simplify your IT operations, reduce repetitive work, and make data-driven decisions.
Freshservice integrations
Integrate Freshservice with cloud and on-premise enterprise applications—with minimal complexity for faster time to value and higher productivity.
Explore integrationsMicrosoft Teams
Get alerts, create or update tickets, see customer details, automate workflows, and more.
Slack
Create and update tickets, send automatic notifications, and sync tickets between tools.
Device42, a Freshworks company
Freshservice works smoothly with Device42 to enable easier CMDB and dependency mapping.
Zoom
Resolve issues faster, generate meeting links in tickets, and use screen sharing and remote control.
AWS
Bring your virtual assets into the CMDB and associate them with Tickets, Problems, Changes, and Releases.
Google Workspace
Import Google Workspace users as requesters and synchronize Workspace updates with Freshservice.
Freshservice has opened up our eyes to deploying new processes in a new fashion. We’re no longer constrained by our legacy ITSM system. Freshservice automation gives us peace of mind.
The experts agree
Industry authorities and customers recognize Freshservice for its superior combination of built-in AI, usability, scalability, and value.
Take a fresh approach to IT services
See what refreshingly easy ITSM can do for your business.