17 Best help desk ticketing systems in 2024
Explore our comprehensive ticketing system guide. Compare the top 17 ticketing systems to find the perfect fit for your customer support needs.
For Free. No Credit Card Required.
Nov 05, 202424 MIN READ
With so many products, services, and systems in use across today’s business landscape, it’s only natural that more issues will arise. With an increased volume of inquiries and requests constantly arriving from all channels, proper processes must be in place to handle them effectively. To tackle these challenges, ticketing software provides organizations with a tool to receive, consolidate, and prioritize all support requests to resolve them quickly, efficiently, and accurately.
Today, we’ll explore help desk ticketing systems, their benefits for modern organizations, and the best software currently available in the market.
What is a ticketing system?
A ticketing system is a software-based solution designed to manage handling various inquiries and issues. It is a centralized platform for tracking these interactions from initiation to resolution. Typically utilized by customer support teams, and various service-oriented industries, a help desk ticketing system allows users to create, prioritize, and assign requests efficiently.
17 Best ticketing systems in 2024
1. Freshdesk
Freshdesk is an AI-powered help desk software from Freshworks designed for ticketing, ease of use, and rapid resolution of customer complaints. With seamless ticketing experiences and self-service options across various channels, it improves customer support operations. Freshdesk's AI-driven automation routes tickets intelligently, ensuring smooth collaboration among team members for swift and precise resolutions. With Freshworks' built-in AI engine, Freddy AI, Freshdesk enables agents to deliver outstanding service consistently, delighting customers every time.
Key ticketing system features:
Self-service: Launch self-service options and help customers find answers on their own.
Workflow automations: Automate routine, time-consuming tasks to improve team efficiency
SLA management: Ensure customers get responses and resolutions on time by setting up SLA reminders and escalations.
Agent productivity features: Enable agents to perform at their level best with canned responses, custom views within the ticketing platform, scenario automations, and in-app notifications.
CSAT: Track and manage customer satisfaction with feedback forms.
Collaboration: Enable your team to collaborate with each other and resolve customer issues faster.
Reporting: Get insights on customer service performance and KPIs with reports and live dashboards.
Marketplace: A diverse range of applications (WFM, field service, telephony, chatbots, etc.) accessible in one unified platform.
Mobile app: Support on the go with the Freshdesk mobile app available on Android and Apple
Sign up for Freshdesk free trial
Pricing
Pricing starts from: $0
Free trial period: 14 days
Advantages:
Reduced Ticket Volume: Empower customers with a self-service knowledge base, deflecting repetitive complaints and freeing agents for complex issues.
Improved Agent Productivity: Automated workflows, collaboration tools, and AI-powered assistance empower agents to resolve issues faster and focus on delivering exceptional service.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Offer a convenient and consistent customer experience across all channels, leading to happier and more loyal customers.
Why customers rave about Freshdesk?
Freshdesk offers a modern and intuitive user-friendly interface that makes it easier for agents to navigate and manage tickets.
“The product maintains a record of customer interactions so you can respond efficiently to new requests and manage the resolution of issues. It allows you to effectively track a large number of customer interactions and easily manage them. We manage about 49 interactions per week, and this product makes it easy to keep track of all these conversations.” — Verified user review, Trust Radius
2. Help Scout
Help Scout is a customer support platform that offers a shared inbox, help center, and live chat software to assist in efficiently managing all customer communications.
Key features
Automated workflows
Easily ‘@’ team members
Collision-free inbox
Individual and team assignments
Pros:
Real-time chat and a robust knowledge base enable quick and accurate responses.
Ease of use and implementation is ideal for non-technical agents.
Cons:
Lack of integration with popular third-party platforms, like Salesforce
The docs feature is outdated and lacks certain useful features
3. Zoho Desk
Zoho Desk helps businesses manage customer communication via phone, email, live chat, SMS text, social media, and more. It also excels at assigning calls to agents based on their department or familiarity with a repeat user.
Key features
Reply assistant
Field predictions
Ticket assignment
Notification rules
Pros:
Knowledge base, community, and embeddable self-service empower users to resolve issues autonomously.
A vast array of productivity tools like work modes and teams can improve operational efficiency.
Cons:
Some of the most helpful automation features within ticketing platforms are only available with the most expensive plan. Integration with existing infrastructure may prove to be challenging.
Integration with existing infrastructure may prove to be challenging.
4. Kayako
Kayako is a customer service software focused on enhancing agent productivity and building customer loyalty. By offering custom views, tags, and conversation assignments, support teams can better track open requests and assign conversations to the right reps.
Key features
Self-help knowledge base
Customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores
Self-service ticket status
SLA notifications
Pros:
Easily view all customer interactions in a single location with Customer Journey SingleView.
Extensive automated workflows can route conversations, resolve common issues, and update statuses.
Cons:
Distributing and receiving large emails can sometimes be an issue
Multi-channel reporting only available with top-tier plan
5. Zendesk
Zendesk is an AI-powered support platform offering a straightforward interface that’s easy to scale as a business grows. It leverages extensive automation features for service teams to enhance and expedite operations.
Key features
Conditional ticket fields
Multiple ticket forms
Skills-based routing
Customizable triggers
Perfect for:
Companies desiring a solution with robust omnichannel capacity that always keeps end-users updated on ticket progress
Pros:
Extremely customizable dashboards that can be tailored to provide insights into the most relevant KPIs
Capable AI chatbots enhance self-service options and improve response times.
Cons:
Starter plan pricing may be prohibitive for startups and small businesses
An overabundance of features and a stodgy interface result in a poor UX
6. HappyFox
HappyFox is a help desk software that emphasizes multi-channel support for tickets arriving via email, web, phone, and social media. It’s integrated with various business applications for accounting, feedback, CRM, commerce, and more.
Key features
Private collaboration notes
Ticket templates
Task management
Canned responses
Perfect for:
Any-sized organization looking to employ ticketing systems for department-specific processes
Pros:
Flexibility in offering agent-based pricing and unlimited agent packages may provide better value for large enterprises.
Distinct software for customer support, IT operations, human resources (HR), and all teams to ensure solutions meet specific needs
Cons:
Limited social media integration can restrict omnichannel approaches
SMS and chat come at an extra fee, further complicating omnichannel strategies
7. Front
Front is a customer operations platform that combines support and sales efforts to deliver sufficient service at scale. It optimizes customer communication by merging help desk and email capabilities with automated workflows and real-time collaboration for support agents.
Key ticketing features:
No-code workflow automation
Smart rules
AI chatbots and agent assistance
Auto-tags
Perfect for:
Businesses looking for a comprehensive communication platform while managing the significant monthly fees
Pros:
Seamless escalations can ensure interactions are transferred from a chatbot or another agent without losing context.
Significant workload balancing capacity ensures that employees don’t experience burnout and no ticket falls through the cracks.
Cons:
It is quite pricey across the board, particularly for the high-end package
Limited knowledge base can restrict chatbot and self-service capacity
8. ProProfs Help Desk
ProProfs Help Desk is a cloud-based support platform designed to help businesses build relationships with users. It provides a centralized dashboard, helping companies handle both internal and external requests more efficiently.
Key ticketing features:
Straightforward ticket prioritization
Shared ticket ownership
SLA monitoring
Parent-child ticketing
Perfect for:
Mid-sized businesses seeking an affordable ticketing system that’s highly integrable with email platforms
Pros:
Automated ticket assignments, security updates, and chatbots help expedite repetitive processes, freeing up availability for live reps.
Extensive live chat capacity enables real-time communication to quicken responses and resolution times.
Cons:
No merge option to consolidate multiple tickets from the same end-user
Lack of integration capacity may pose challenges in connecting with existing infrastructure
9. HubSpot Service Hub
HubSpot's Service Hub is an AI-powered customer service solution that delivers support at scale with unified customer insights. It provides impactful self-service tools and an omni-channel help desk that unifies tasks to facilitate prioritization.
Key ticketing features:
Playbooks
Conversation intelligence
Shared inbox
Ticket routing and automation
Perfect for:
Companies wanting a highly integrable solution that offers distinct plans for establishments of any size
Pros:
Excellent internal communication tools that enhance transparency between service and sales teams
An integrated content management system (CMS) promotes more personalized interactions based on visitor behavior and interests.
Cons:
Plans are only available as annual commitments, which means you can’t get out early if you don’t like the platform
Though lower-tier plans are affordable at first glance, extra features and third-party integration fees can add up quickly.
10. LiveAgent
LiveAgent is a full-featured help desk and live-chat software designed to personalize customer interactions. It offers a capable chat widget, while also providing an omnichannel universal inbox, built-in call center, and robust customer service portal.
Key ticketing features:
Internal tickets and notes
Universal inbox
Canned responses
Multilingual support – 43 languages available
Perfect for:
Large organizations with global client bases seeking to enhance real-time communication
Pros:
The customer portal, knowledge base, forums, and FAQs provide ample self-service options for users to answer queries independently
Strong email synchronization offers message forwarding, notifications, templates, and exporting.
Cons:
The mobile app could be improved, particularly in its navigability
Lack of integration with CRM systems can create gaps in workflow
11. AzureDesk
AzureDesk is a help desk system that provides users with easy access to pertinent information and support. It centralizes all customer-facing information for a more strategic customer service approach.
Key ticketing features:
Unlimited mailbox
Ticket fields
Ticket tracking
Self-service portal
Perfect for:
Companies looking for an easy-to-use, broad solution that can be employed for general ticketing processes
Pros:
Ask questions, make suggestions, seek advice, or review messages with private internal notes.
Custom tags can improve handling and understanding of tickets when handling high volumes of requests.
Cons:
The one-size-fits-all plan may limit its application for businesses of specific sizes and specialities.
Restricted customization, while available features are complicated to utilize
12. SpiceWorks
Spiceworks help desk is purpose-built for IT pros, aiming to promote improved internal IT support. It assists in managing tickets, providing omni-channel support, and tracking agents’ performance.
Key ticketing features:
Knowledge base
Automated responses
Customizable web portal
Advanced reporting capacity
Perfect for:
Smaller organizations operating a tight budget that still desire a basic ticketing system
Pros:
Offers both web and self-hosted versions
Ability to generate multiple ticket templates to capture relevant details from unique users
Cons:
Inventory system sometimes produces inaccurate information
Lags behind similar systems in ability to unify tickets from all channels in a single location
13. SupportBee
SupportBee is a web-based email support tool that assists companies in organizing their customer service emails efficiently. Multiple teams can collaborate on cases, correlate all support emails in a single system, and collect contacts from multiple addresses and forms.
Key ticketing features:
Shared inbox
Knowledge base
Customer portal
Private notes
Perfect for:
Small companies that emphasize email as their main communication channel
Pros:
Available through desktop, mobile, and within your existing email platform, promoting accessibility from any location
Workflow is very similar to email, resulting in the reduced learning curve.
Cons:
High volumes of incoming emails can occasionally cause the platform to lag
While very affordable, it does come at the expense of useful features that can be found in similar solutions
14. Vision Helpdesk
Vision Helpdesk is a multi-functional help desk, service desk, and live chat software that provides tools for companies to manage their customer support and IT resources efficiently.
Key ticketing features:
SLA rules
Ticket properties customization
Automated client notifications
Ticket auto-close
Perfect for:
Organizations want a system that offers a vast array of proactive automation capabilities while also working with a smaller budget
Pros:
Round-robin or rule-based distribution is available to balance agent workloads while still ensuring end-users are connected to relevant personnel
Extensive omnichannel potential through email, call, chat, social media, and APIs
Cons:
A lack of default reports can limit analytics and insights capabilities
Dated interface that weakens UX
15. Jira Service Management
Jira Service Management allows for easy receiving, tracking, and managing of end-user requests. It offers straightforward categorization of service incidents and changes by organizing and prioritizing tickets in a single place.
Key ticketing features:
AI-powered AI agent
No-code dynamic forms
Request queues
SLA management
Perfect for:
Organizations desiring a full ITSM solution in addition to ticketing and help desk software
Pros:
Comprehensive customer support and ITSM capabilities can enhance cost optimization if you plan on utilizing all of its features
Single source of truth where end-users can report a ticket and access a knowledge base from the same platform
Cons:
Not ideal for using as a project management ticketing system
Limited capacity to generate robust customer profiles, restricting personalization efforts
16. Hiver
Hiver is a collaboration platform that assists organizations in engaging with customers, employees, and vendors. It provides multi-channel communication abilities, self-service features, and robust automation capacity to ensure all issues are taken care of quickly and accurately.
Key ticketing features:
Automated reminder emails
SLA monitoring
Automated ticket closing
Prevents duplicate replies
Perfect for:
Businesses focused on email communications who already utilize the Gmail platform
Pros:
Enhance collaboration among teams with notes and @mentions to ensure timely and accurate responses
AI assistance can help generate outgoing emails and also summarize incoming messages to reduce manual effort
Cons:
No option to create new tickets unless it’s attached to an email
Lack of distinction between messages creates difficulties in referencing past interactions
17. Team Support
TeamSupport is a comprehensive software solution that manages the entire post-sale customer experience, focusing on revenue growth, reduced churn, and improved satisfaction.
Key features
Suggested solutions
Sentiment analysis
Ticket collision prevention
Related tickets
Perfect for:
Businesses desiring a dynamic solution that offers use for the entire customer life cycle
Pros:
Powerful search tool assists in quickly and easily locating tickets, knowledge base entries, and wiki articles
Ability to define custom ticket types, ticket tags, and action types to meet unique support needs
Cons:
Clunky interface with an excess of features that can limit its usefulness for organizations operating in niche spaces
Tickets are automatically rearranged based on priority, which can lead to long wait times for customers if agents aren’t always attentive.
What are the different types of customer service ticketing systems?
Different ticketing systems can enhance support in various business efforts. When researching and selecting a provider, make sure that its help desk ticketing features are well-suited to your unique organizational needs. Now let’s take a look at the different types of ticketing systems.
Help desk ticketing system
While customer service ticketing systems encompass many customer interactions, help desk ticketing systems are tailored specifically for technical support and service management.
Help desk platforms serve as a centralized platform where users, whether they’re internal employees or external customers, can submit their requests or report problems. Each submitted request is logged as a ticket containing the requester's contact details, a description of the issue, and its current status. Agents utilize the ticketing system to track, prioritize, and assign tickets to the appropriate support agents, ensuring that problems are addressed on time and within specified service level agreements (SLAs).
Customer service ticketing systems
Customer service ticketing systems usually initiate support tickets when an individual contacts the customer service team via email, phone, live chat, or social media. These requests are then routed to specific agents with the appropriate expertise to address the issue, ensuring that each inquiry receives prompt attention from the right support agent.
For instance, a customer may submit a ticket through an electronics retailer’s online customer support portal reporting a critical issue with a recently purchased laptop. The ticket is automatically categorized as a ‘hardware problem’ and prioritized as ‘urgent.’ A qualified hardware technician will review the ticket, gather additional information, and diagnose the problem remotely.
Software development ticketing systems
Software development tickets may originate from stakeholders, such as product managers or clients. They generally contain information such as the task description, priority, assignee, and any relevant dependencies.
For instance, a product manager can submit a request for a new feature that allows users to filter search results based on location in a mobile application. The ticket is designated as a ‘feature request’ and classified as ‘high priority’ due to its importance for enhancing user experience (UX). The development team then reviews the ticket and assigns the task to a front-end developer with experience in mobile app development.
What are the benefits of ticketing systems?
Ticketing systems provide multiple benefits to businesses of all sizes. Whether your company is a one-person online storefront, a mid-market business, or an enterprise grade consumer goods retailer, ticketing systems can offer massive value for money and streamline your customer support operations. The exact benefits will depend on how you plan to utilize the application, but, in general, may include:
Improved organization and efficiency: By centralizing information and automating workflows, ticketing systems streamline processes, reduce manual effort, and ensure that tasks are promptly addressed.
Enhanced accountability: Ticketing software promotes accountability by documenting all actions and resolutions related to each ticket. Stakeholders can easily access ticket histories to review progress, monitor performance, and verify SLA compliance.
Improved collaboration: A centralized platform for sharing information, updates, and feedback can enhance collaboration among team members. Employees can coordinate efforts to resolve issues more efficiently through ticketing features such as comments, notifications, and real-time messaging.
Data-driven insights: Ticketing systems generate valuable data that can be used to analyze trends and measure key performance indicators (KPIs). Assessing relevant metrics helps organizations gain a deeper understanding of their operations and identify opportunities for improvement.
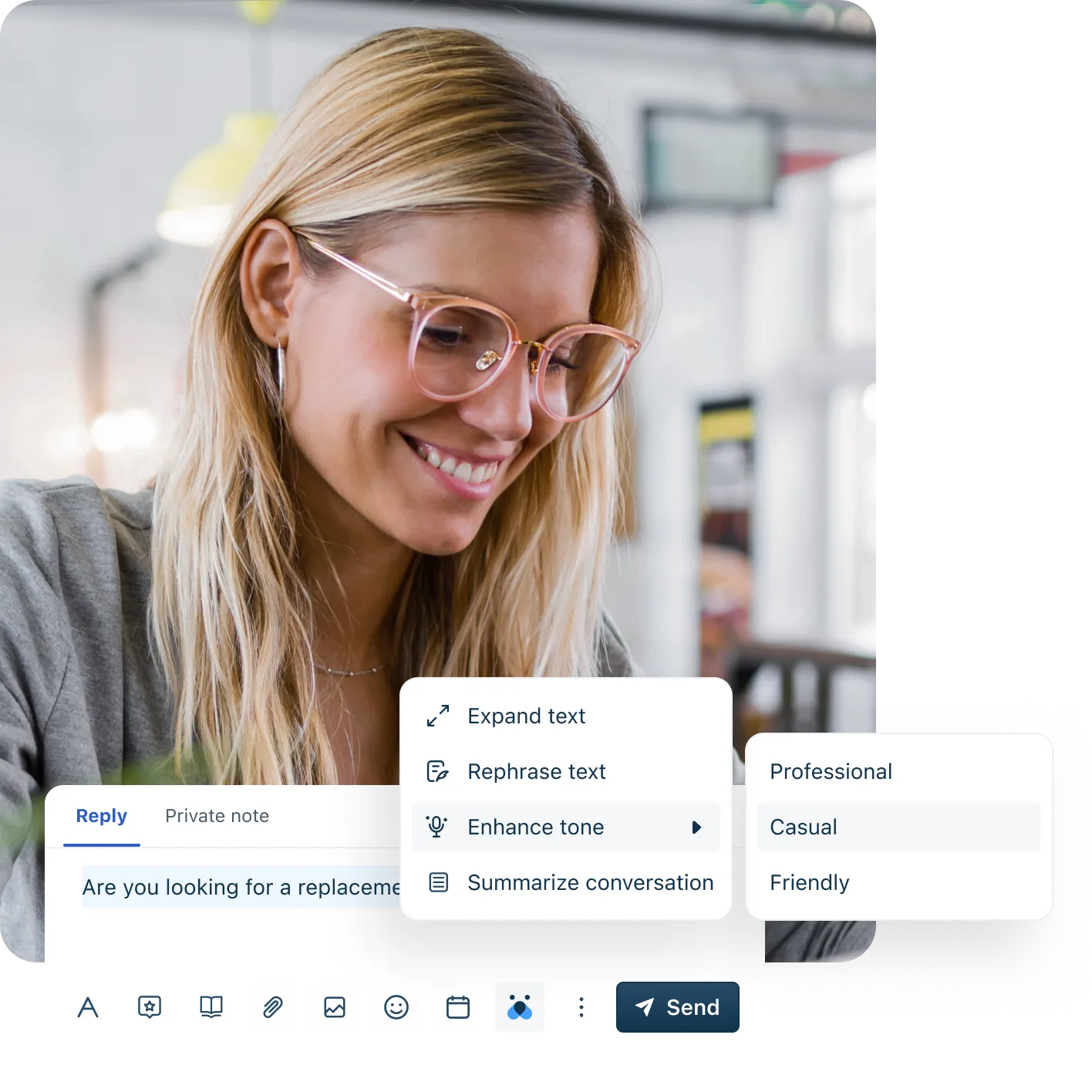
Essential features of help desk ticketing software
Distinct providers will offer varying ticketing tools based on their area of focus; some may have a tunnel vision on support, while others may be broader in scope. You’ll want to ensure that the software you employ provides features relevant to your business requirements.
Common attributes of ticketing software may include:
Multi-channel support
Ticketing systems are versatile in their ability to be integrated across various communication channels to manage requests from different sources. Whether emails, phone calls, social media messages, or live chats, ticketing software can centralize incoming interactions from multiple channels into a single platform. This unified approach ensures that all customer inquiries are captured and tracked consistently, regardless of the channel through which they were received.
Ticket assignment, prioritization, and ticket views
Ticket assignment involves routing incoming tickets to the most appropriate personnel or teams based on predefined rules or criteria like skill, workload, or even round-robin. Once distributed, prioritization functionalities allow for the categorisation of requests based on urgency or impact. Straightforward visual representations of priorities, such as colour-coded labels or filters, further facilitate efficient task management and decision-making.
Automation capabilities
Automation streamlines ticket creation by allowing for predefined templates and rules. When a user submits a request, the system can automatically categorize it based on predefined criteria such as keywords, user information, or history. This reduces manual effort and ensures tickets are appropriately tagged for faster resolution.
SLA management
Ticketing software makes it easy to define SLAs for different types of tickets. This may involve setting response time goals and resolution targets based on the level of service stakeholders anticipate. Establishing clear SLAs strengthens agents’ and end-users' understanding of the expected service standards.
Agent productivity
Ticketing systems often include internal communication tools such as chat functionalities and internal notes, collaboration tools, and AI-powered tools within requests. These features empower agents to resolve complex issues more efficiently, share insights, and provide assistance when needed. Many systems also offer knowledge bases, where team members can access articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides.
Self-service options
Self-service portals where users can submit their tickets and access self-help resources are also often included in ticketing systems. These portals may provide forms that guide users through relevant information to expedite the resolution process. Additionally, individuals can track the status of their tickets, view past interactions, and communicate with support agents if needed, all within the self-service portal.
Integrations for rich customer context
Customer relationship management (CRM) software is commonly integrated with ticketing systems to give agents sufficient data to personalize their interactions. This connection consolidates support tickets into the CRM system alongside other customer information such as contact details, purchase history, and preferences. By unifying this data into a single repository, representatives gain a holistic view of each user's journey, allowing for more targeted communication.
Help desk ticketing reports and analytics
Ticketing systems allow organizations to easily generate custom dashboards tailored to their specific objectives. The software typically allows users to create custom reports by selecting relevant data fields, applying filters, and visualizing data in various formats. These analytics may provide insights into customer demographics, ticket trends, or the effectiveness of support channels.
AI capabilities
Since the advent of conversational AI, ticketing systems have made significant progress in delivering improving customer experiences. Chatbots and virtual assistants use generative AI and natural language processing (NLP) to interpret human language and guide users through troubleshooting steps. Predictive analytics in modern ticketing systems offer advanced insights and custom dashboards that make decision-making fast and simple.
Best practices for ticketing systems
Competent ticketing systems often provide enhanced flexibility, allowing businesses to mold it to fit their specific business goals. But there are some standardized practices you’ll want to employ to ensure that your system is operating to the best of its potential.
Define clear goals: Understand why you need a ticketing system. Designating clear objectives will guide your implementation process, whether it's for customer service, or project management.
Customize ticket categories: Tailor categories and priorities to suit your organization's needs. This helps streamline ticket management while verifying that each request receives appropriate attention.
Set SLAs: Establish service agreements to define response times for different requests. This establishes expectations for customers and support teams while helping prioritize tasks efficiently.
Regularly review: Continuously monitor your ticketing processes, workflows, and system configurations to identify opportunities for refinement. Embrace feedback from stakeholders to drive ongoing improvements.
How to implement a ticketing system?
Integrating a ticketing system into existing organizational infrastructure can often be intimidating. But it doesn’t have to be – with sufficient research, planning, and support, most businesses find the help desk ticketing system implementation process to be more straightforward than they anticipated.
Connect your support channels.
Firstly, integratemessaging channels like email, phone, chat, and social media with the ticketing platform. Assess which channels users most frequently leverage to determine which ones to integrate. Select a provider that offers integration capabilities with these channels or supports third-party integrations.
Set up SLA policies and targets.
After integrating relevant channels, you’ll need to set appropriate SLA policies to communicate clear expectations to your staff and end-users. To achieve this, identify ticket priorities based on factors such as urgency, impact on business operations, and customer needs. For example, critical issues affecting production systems may be prioritized over routine inquiries. Once ticket categories are established, define specific targets for each one, including initial response and resolution times.
Bring in your support team.
Next, you should consult your support team to gather their input on current pain points and requirements. Once a ticketing system meets their needs, be sure to offer sufficient training and onboarding sessions to familiarize them with the new software. Remember to tailor the training to address specific responsibilities within the support team, such as ticket categorization, prioritization, and SLA management.
Configure support workflows and automation
First, map out your organization's existing workflows for handling support requests. Define roles for each stage, including support agents, supervisors, and stakeholders. Then, configure the help desk ticketing system to mirror these workflows, creating custom ticket categories and fields to align with your specific needs.
Additionally, most ticketing systems provide robust automation features to eliminate manual tasks and streamline repetitive processes. Identify routine activities ideal for automation, such as ticket routing, prioritization, status updates, and notifications.
Add customer contacts and integrate other business tools.
Existing contact data should be imported into the help desk ticketing system, while customers should also be able to submit their own information directly when creating tickets. Create a centralized database of contacts within the ticketing software, including names, emails, phone numbers, and organization affiliations.
Integrating your ticketing system with existing tools and software can enhance customer information. Identify key platforms used within your organization, such as CRM systems, project management tools, and monitoring software.
Define support metrics to be tracked.
Identifying which metrics to track involves understanding the KPIs that align with your organization's goals and customer expectations. For instance, a business struggling with slow resolution times will likely want to monitor its average response times and mean time to resolution (MTTR). To expedite resolution processes, the company may refine its routing strategy, enhance its knowledge base, or optimize escalation protocols.
How are different industries using helpdesk ticketing systems?
Retail & ecommerce
Suppose a customer purchases a product from an online store but needs help with the product, such as a missing component, the consumer submits a support ticket through the e-commerce platform's support portal, detailing the issue and providing relevant order information. This ticket is then automatically categorized and assigned to the appropriate agent. The representative then investigates the issues, providing updates on the investigation status and resolving the problem promptly.
Travel & hospitality
Imagine a scenario where a hotel's computer system experiences a technical glitch, preventing staff from checking-in guests. A hotel staff member registers a support ticket through their helpdesk portal, describing the issue’s impact on operations. The ticketing system will immediately prioritize the ticket ‘high’ based on its severity, distributing it to the relevant support team. They’ll acknowledge the ticket, examine the root cause of the problem, and implement a solution to restore service.
Education
Consider a university professor who submits a ticket requesting a custom application to support a research project. The ticketing system categorizes the request and assigns it to the appropriate development team. Team members will then collaborate with the professor to gather additional requirements, design the application, and incorporate the necessary functionalities.
Banking & finance
Let’s say that a banking institution wants to implement a new online feature to enhance customer experience (CX). The request is submitted, and the ticketing system categorizes the request as a project, allowing for the creation of a project plan and setting milestones for development. Throughout the project lifecycle, stakeholders from different departments collaborate through the ticketing system, reviewing progress and addressing issues as they arise. The system also assesses timelines, budgets, and deliverables, enabling managers to identify risks and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
Healthcare
For a healthcare provider, a user may submit a ticket requesting support in updating their contact information. Since this issue is likely to be considered low priority compared to other incoming tickets, it’s automatically prioritized as such, ensuring that it’s still handled in a timely manner but not before more urgent scenarios. A support agent will acknowledge the ticket, verify the patient's identity, and process the requested changes as soon as time allows and by privacy regulations.
Manufacturing
Suppose a manufacturing company is launching a new product line and needs to coordinate various tasks across different departments. The project manager creates a ticket for each task within the project, detailing requirements and deadlines. Throughout the project, the ticketing system tracks resource allocation and team productivity, allowing the manager to identify bottlenecks and ensure alignment with overall objectives.
How to combat common challenges with ticket management systems?
As with any new system, some difficulties may arise when using help desk ticketing management software. If they do, remember that most can be swiftly resolved with a little attention to detail, problem-solving acumen, and teamwork.
Overwhelming ticket volume: Many incoming tickets can occasionally overwhelm support teams. Automation features should be implemented to streamline routing and prioritization to address this. You can also set up triggers to automatically assign tickets, escalate urgent issues, and send notifications to relevant stakeholders.
Lack of integration: If the ticketing system isn’t connected with other relevant tools, it may lead to operational inefficiencies. Integrate your system with CRM software, communication channels, project management platforms, and other applications. APIs, third-party connectors, or built-in integrations can also be leveraged to facilitate data exchange between disparate systems.
Inadequate reporting: Measuring performance and making data-driven decisions can be challenging without robust analytics capabilities. You should customize your ticketing dashboards to track key metrics critical to overall goals. Regularly examine these KPIs to identify areas for improvement and ensure resources are being allocated effectively.
Security concerns: When using a ticketing system, security breaches or non-compliance with regulations can pose significant risks to your organization. It’s critical to implement adequate encryption, access controls, and user authentication mechanisms to combat these challenges. Remember to update the system regularly to address security vulnerabilities and adhere to industry best practices.
How do you choose the best ticketing system software for your business?
When selecting a ticketing software from the list above, it’s crucial first to assess your business requirements to recognize which specific features to seek out. In general, companies across all industries will benefit from an easy-to-use, highly integrable, and scalable ticketing system.
Evaluate ticketing needs
First, analyze the expected volume and complexity of tickets and the types of issues to be managed. This will help determine whether you require a system with broad or narrower functionalities and what type of subscription or service package you need. Don’t forget to seek feedback from potential users within the organization to understand their preferences. Once you’ve considered these factors, compare features, UX, and support options to determine which provider best fits your company.
Ease of use & implementation
Start by evaluating the user interface (UI) of potential ticketing systems. Look for intuitive designs that facilitate easy access to essential functionalities. Actively evaluate how user-friendly the system is for both employees and customers.
Then, assess the level of support the provider offers, including documentation, training resources, and customer support channels. Identify systems that offer comprehensive implementation assistance, including guidance on data migration, customization options, and integration with existing platforms.
Scalability
Examine each ticketing software's capacity to handle increasing volumes of requests over time. This may involve assessing whether its infrastructure is designed to scale horizontally or vertically to meet growing demands. Seek out load balancing and clustering features that enable systems to distribute workloads efficiently and maintain responsiveness as volume increases.
Automation & time saved
To identify the automation tools most beneficial to you, you must first identify the most repetitive tasks involved in managing your support tickets. Examine the range of features each provider offers, such as workflow automation, rule-based triggers, and ticket auto-assignment. Your organization may be keen on optimizing particular processes, such as routing, prioritization, or responses, to free up time for your real-world team to focus on more complex activities.
Integrations
It’s paramount to sufficiently evaluate the compatibility of each potential ticketing system with your existing technologies, considering supported integration protocols, APIs, and pre-built connectors. For instance, connection with an email platform can provide the ability to automatically convert emails into support tickets, allowing agents to manage them within the ticketing system. Other popular integrations include CRM software, knowledge bases, bug tracking systems, and more.
Measuring ROI
For starters, you’ll need to know the total cost of ownership (TCO) for implementing and maintaining the ticketing software to assess your return on investment (ROI) accurately. Consider upfront expenses and ongoing costs such as subscription fees, training, and support. Then, compare the TCO against the expected benefits of improved operational efficiency, reduced support costs, and increased user retention. By conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, you can determine an approximate ROI before committing to a contract.
Ready for easy-to-use, intuitive helpdesk ticketing software?
Related resources
Choosing the Right Helpdesk Software
Explore our guide to selecting the best helpdesk software for your business and enhance your customer service strategy.
Explore Freshdesk's Helpdesk Features
Discover powerful helpdesk features designed to streamline customer support and improve team productivity with Freshdesk.
Master Helpdesk Software Best Practices
Learn essential best practices for optimizing helpdesk software and delivering exceptional customer support.
FAQ
Which ticketing tool is best?
Freshdesk is widely considered one of the best ticketing tools available, especially for businesses seeking an intuitive and user-friendly platform. It offers robust features like automated workflows, multi-channel support, and detailed analytics, making it a top choice for improving customer support. Other tools like Zendesk and Jira Service Desk are also popular, but Freshdesk stands out for its ease of use and comprehensive feature set.
Is a ticketing system a CRM?
Not exactly. A ticketing system handles customer support requests, while a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) tool covers a broader scope, including sales and marketing. However, they often work together to give your customers a better overall experience.
What are the steps in a ticketing system?
In a ticketing system, the process usually starts with creating a ticket, then categorizing and assigning it to the right team. After that, it’s all about resolving the issue and closing the ticket. Some systems also include steps for escalating issues, communicating with customers, and tracking progress.
What is called ticketing?
Ticketing is the process of managing customer questions or problems by turning each one into a "ticket." This way, every issue is tracked from start to finish, making sure nothing falls through the cracks and customers get the help they need.